Heart diseases continue to be one of the leading causes of death worldwide. More often now that we live in a world that is an overachiever, the lifestyle here is fast and overwhelming. People usually ignore their health and warning signs until it’s too late. One of the most dangerous conditions is heart blockage, which occurs when the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. However, early detection is critical. Experts stress that recognizing symptoms can make the difference between timely intervention and a fatal cardiac event.As a landmark study in the New England Journal of Medicine found, close to one-third of patients suffering from a heart attack didn’t have chest pain. They just had some sort of shortness of breath, tiredness, or nausea, so early diagnosis became all the more important, particularly for women and the elderly.Here are eight warning signs of heart blockage that you should never ignore if you experience them.
Chest discomfort or pain (Angina)
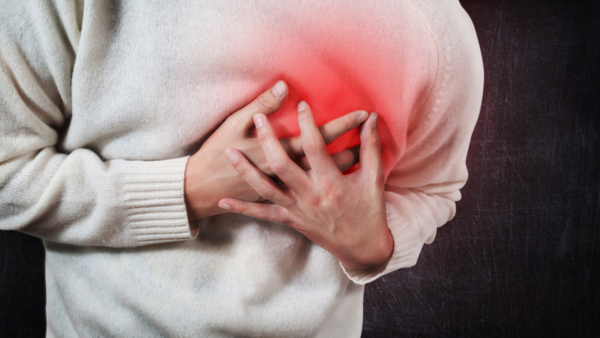
Most people who experience heart blockage have chest discomfort or pain. It may be pressure, tightness, or a feeling of heaviness in the chest, usually brought on by exercise or stress. This is because the heart muscle does not receive sufficient oxygenated blood. When the pain disappears with rest, it might be stable angina, which indicates narrowed coronary arteries.
Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath with even light exertion or at rest indicates that the heart is having trouble circulating blood efficiently. With blockages, the reduction of blood flow means the heart can no longer supply the body’s needs for oxygen and thus brings on breathlessness. The symptom will sometimes intensify over time and is a significant warning signal for underlying heart disease or heart failure.
Unexplained fatigue
Abrupt, intense, or intensifying fatigue that does not decrease with rest could suggest that your heart is malfunctioning. If blood flow to the body is restricted due to blockage, organs and muscles get less oxygen, leading to fatigue even with regular activities. Dismissing this symptom will cause the diagnosis of life-threatening heart disorders to be delayed.
Pain in arms, neck, jaw, or back
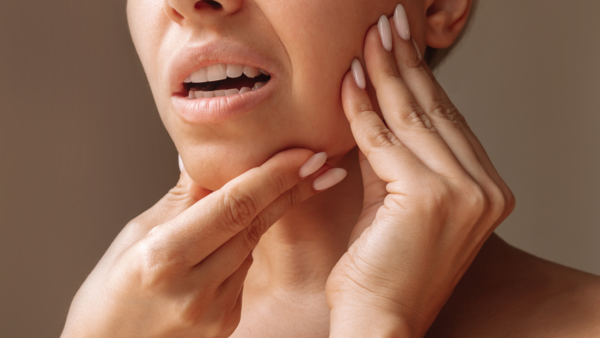
Pain that radiates from the chest to the arms, neck, jaw, or back may indicate a heart attack or coronary artery blockage. It is a more frequent symptom in women and is frequently confused with muscular or nerve pain. Identification of this referred pain is important, as it indicates ischemia in areas innervated by the same nerves as the heart.
Sweating without physical activity
Unusual cold sweats without exertion or exposure to heat could be an indicator of heart distress. Such a symptom arises as a response from the body due to stress caused by inadequate blood circulation and lack of oxygen in the heart. Sudden, excessive sweats with other signs and symptoms should trigger urgent medical assessment for cardiac incidents.
Nausea or dizziness

Dizziness, lightheadedness, or nausea may be a sign of too little blood reaching the brain and other organs because of blocked blood vessels in the heart. Vomiting usually accompanies these, and they may increase with activity. When added to chest pain or shortness of breath, they are highly suspicious of an emergent cardiovascular condition that needs to be treated immediately.
Irregular heartbeat (Arrhythmia)
An irregular heartbeat, such as skipped beats, palpitations, or a rapid pulse, can occur when the heart is oxygen-starved from clogged arteries. Arrhythmias may be harmless but also potentially life-threatening and usually indicate that the electrical system of the heart is compromised. Persisting or new arrhythmias should be evaluated by a cardiologist to avoid complications.
Swelling in the legs or feet (Edema)
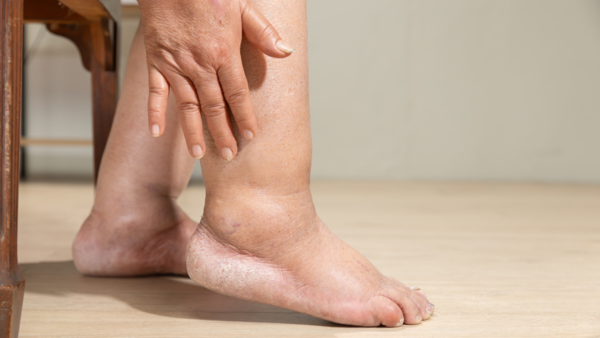
Lower extremity swelling results from inefficient pumping of blood by the heart, which leads to the accumulation of fluid in tissues. It is a frequent occurrence with congestive heart failure that may arise as a complication of chronic coronary artery disease. Chronic edema that is associated with other manifestations of the heart should be pursued aggressively in order to treat the heart.images: canva




